Definition
In math, a vector is object that has a magnitude and a direction. The components of a vector are the numbers that describe the vector in a coordinate system. A common coordinate system is the Cartesian coordinate system which uses the x, y, and z axes.
In programming, we can implement a vector as an array of numbers. A 2D vector, for example, can be defined as an array of 2 floats. A 3D vector can be defined as an array of 3 floats.
vec2 = [x, y]
vec3 = [x, y, z]
The x, y, and z are the components of the vector.
Addition & Subtraction
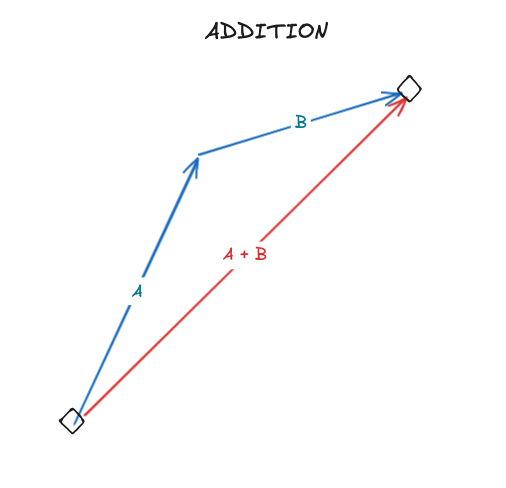
Addition and subtraction of vectors can be done by adding or subtracting the corresponding elements of the vectors.
a = [ax, ay]
b = [bx, by]
a + b = [ax + bx, ay + by]
a - b = [ax - bx, ay - by]
Scalar Multiplication & Division
The scalar multiplication, also know as Vector Scaling, of a vector is done by multiplying each component of the vector by the scalar.
a = [ax, ay]
scalar = 2
a * scalar = [ax * scalar, ay * scalar]
The division of a vector by a scalar is done by dividing each component of the vector by the scalar.
a = [ax, ay]
scalar = 2
a / scalar = [ax / scalar, ay / scalar]
Dot Product
The dot product of two vectors, also know as Scalar Product, is a scalar value. It is calculated by multiplying the corresponding elements of the vectors and summing the results.
a = [ax, ay]
b = [bx, by]
dot(a, b) = ax * bx + ay * by
The dot product of two vectors can also be calculated by the magnitude of the vectors multiplied by the cosine of the angle between them.
dot(a, b) = |a| * |b| * cos(theta)
The theta is the angle between the two vectors. The angle is the smallest angle between the two vectors.
Unit Dot Product
Often in computer graphics, we want to do the dot operation between two vectors which one is a unit vector. This operation is useful when we want to project one vector onto another. In other words, how much of a vector is on the axis defined by the unit vector.

Cross Product
The cross product of two vectors, also know as Vector Product, is a vector that is perpendicular to both of the vectors. The magnitude of the cross product is the area of the parallelogram formed by the two vectors. The direction of the cross product is determined by the right-hand rule.

Magnitude
The magnitude of a vector is the length of the vector. We can calculate the magnitude of a vector using the Pythagorean theorem.
magnitude = sqrt(x^2 + y^2)
Unit & Normalized Vector
A unit vector is a vector with a magnitude of 1. We can normalize a vector to get a unit vector.
unit_vector = vector / magnitude(vector)
Normal
A normal is a vector that is perpendicular to a surface. Don’t confuse it with the normalized vector.